Wrists: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
#[[Registration]] | #[[Registration]] | ||
#cartilage building | #cartilage building | ||
#"wiggling" bones around | #"wiggling" bones around | ||
#ligament length measures | #ligament length measures | ||
#<fill in with more tools..> | #<fill in with more tools..> | ||
Revision as of 19:33, 4 May 2009
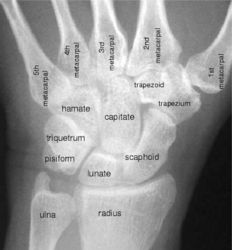
The wrist is a diarthrodial anatomical joint consisting of 8 small bones (scaphoid, capitate, hamate, lunate, trapezium, trapezoid, triquetrum, pisiform) and 7 long bones (radius, ulna, and 5 metacarpals). When subject to injury and disease the wrist undergoes changes in kinematics, inter-bone joint space areas, cartilage thickness, length of ligament paths, etc. Developing computational tools for the analysis of anatomical joint characteristics is important in understanding the cause of injury, tracing the progress of disease, and taking preventative measures.
-
X-ray of the wrist with bone names
-
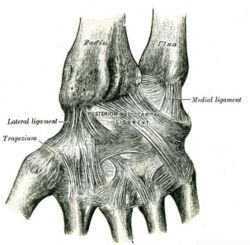
Ligaments: posterior view of left wrist
Overall Pipeline
- Data acquisition
- Segmentation of neutral wrist
- Registration of non-neutral positions
- Retrieval of kinematics
- Inter-bone joint space area calculations
- Ligament path calculations
- Cartilage maps (location & thickness)
- Cartilage surface deformations
- Joint simulation
Tools
- Registration
- cartilage building
- "wiggling" bones around
- ligament length measures
- <fill in with more tools..>